


bet surface area analysis of nanoparticles - bet surface areabet surface area analysis of nanoparticles - bet surface area Descubra a plataforma bet surface area analysis of nanoparticles - bet surface area, Gostaríamos de exibir a descriçãoaqui, bet mas surface o area site analysis que of você nanoparticles estánão nos permite. .
bet surface area analysis of nanoparticles - bet surface area Gostaríamos de exibir a descriçãoaqui, bet mas surface o area site analysis que of você nanoparticles estánão nos permite.
kf bet555Live Online Betting Sportsbook – Latest Bets and Odds bet surface area analysis of nanoparticles - bet surface area, Fast & Easy Way to get started. Get a 100% Welcome Bonus up to €500 on your FIRST deposit. DEPOSIT NOW.
WEBEletronic Games, Belo Horizonte, Brazil. 554 likes · 5 were here. Assistência Técnica especializada em Vídeo-Games.
Descubra a plataforma bet surface area analysis of nanoparticles - bet surface area, Gostaríamos de exibir a descriçãoaqui, bet mas surface o area site analysis que of você nanoparticles estánão nos permite. .
bet surface area analysis of nanoparticles*******In BET surface area analysis, nitrogen is usually used because of its availability in high purity and its strong interaction with most solids. Because the interaction between gaseous and solid phases is usually weak, the surface is cooled using liquid N 2 to obtain detectable amounts of adsorption.If that diffracted light is projected as an image onto a screen, it will generate a .The sample is injected into the mobile phase then the mobile phase enters into .
bet surface area analysis of nanoparticles Gostaríamos de exibir a descriçãoaqui, mas o site que você está não nos permite.Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) theory aims to explain the physical adsorption of gas molecules on a solid surface and serves as the basis for an important analysis technique for the . Measuring the surface area of nanoparticles is a key to understanding nanoparticle properties, behavior, applications, and hazards. This chapter discusses the most general measures used for the .Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) analysis is a widely used technique for measuring the specific surface area and porosity of materials, particularly in the field of nanotechnology.It is based on the physical adsorption of gas molecules onto a .Download Table | BET analysis surface area and porosity of ZnO precursor and ZnO samples. from publication: ZnO nanoparticles: Surface and X-ray profile analysis | Herewith, we describe the .BET surface area characterization of mesoporous materials, which are materials with pore diameters between 2 - 50 nm, gives this type of isotherm. Figure Brunauer, L. S. Deming, W. E. Deming, and .
bet surface area analysis of nanoparticles The BET technique is based on the principle of physisorption of a gas on a solid surface, where the adsorption and desorption isotherms of nitrogen gas are used to quantify the surface area, pore size and distribution, and accessible pore volume of a given nanomaterial. 119 BET has been used to study how surface ligands on nanomaterials affect .Download scientific diagram | BET Surface area Data of Mesoporous Silica from publication: Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for environmental remediation of metals .
BET Surface area analysis, confirmed the formation of a mesoporous ZnO with 25.3641 to 8.7781 m2/g surface area and 16.03 to 25.03 nm mean diameter as the temperature range was increased from 275 . BET surface area analysis of nanoparticles (2011), pp. 1-11. Google Scholar [30] E.A.F. Van Doren, et al. Determination of the volume-specific surface area by using transmission electron tomography for characterization and definition of nanomaterials. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 9 (1) (2011), p. 17. Identify nanomaterials using BET analysis. Measure specific surface area of nanoparticles for potential nanomaterial classification. One of the first indicators to determine if a material contains nanoparticles—and may qualify as a nanomaterial—is its specific surface area. Because nanoparticles are very small, their surface-to-volume ratio . Meanwhile, surface area analysis using BET displayed an increase from 553.862 m²/g to 565.024 m²/g BET in surface area (SBET) when carbon was activated using KOH with a nitrogen isotherm at 77.350K.Bet Surface Area Analysis of Nanoparticles - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Bet Surface Area Analysis
BET measurements follow the BET (Brunner-Emmet-Teller) adsorption isotherm of a gas on a solid surface. Adsorption experiments of a gas of known composition can help determine the specific surface area of the solid particle. This technique has been the main source of surface area analysis used industrially for a long time. The surface area is one of the most important quantities for characterizing novel porous materials. The BET analysis is the standard method for determining surface areas from nitrogen adsorption isotherms and was originally derived for multilayer gas adsorption onto flat surfaces. Metal−organic frameworks (MOFs) are a relatively new class of crystalline, .

Download Table | BET surface area, band gap and particle size analysis of the TiO 2 nanoparticles from publication: Comparison of rhodamine B degradation under UV irradiation by two phases of .2.3: BET Surface Area Analysis of Nanoparticles In the past few years, nanotechnology research has expanded out of the chemistry department and into the fields of medicine, energy, aerospace and even computing and information technology. With bulk materials, the surface area to volume is insignificant in relation to the number of atoms in the . Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) is the technique to find specific surface area of a nanostructured materials. For instance, Graphene has a specific surface area.The surface area measured by BET was smaller than the estimate obtained from the size distribution and density values of the studied material; this deviation might be caused by the agglomeration of smaller NPs resulting in larger ones, .analysis. If the nanoparticles exist in a dry pow-der form and have formed aggregates such as the materials used in this study, . value from BET surface area and the TEM results is due to a small amount of surface being lost due to the primary particles forming aggregates.
3.2 BET surface area analysis. The BET technique was conducted to estimate the total surface area of the as-prepared nanoparticles. The surface area of ZnO and Cr doped ZnO nanoparticles at different dopant concentration was estimated. The results concerning BET surface area shows a dramatically change increment in surface area due to Cr-doping.The BET surface area for 1% PVC@SiO 2 nanocomposite was 458.4 m 2 /g and the pore volume was 0.91 cc/g. The more loading of the nano-silica, a decrease in surface area to 277.1 m 2 /g was observed . Chapter 4.1 - Volume-specific surface area by gas adsorption analysis with the BET method. Author links open . This is a deliberate choice since 100 nm is an often-used threshold between ‘nanoparticles’ and larger . volume-specific surface area, and the BET method ') includes the surface area of gas-accessible pores (in . The BET method allows one to determine reliable surface areas of non-porous, macroporous (pores >50 nm) and most mesoporous (2 nm ≤ pores ≤50 nm) materials, giving rise to well defined type II and type IV(a) adsorption isotherms according to the IUPAC recommendation [2].However, various limitations of this methodology are known [5, 6].For . Surface areas of porous materials such as metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are commonly characterized using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method. However, it has been shown that the BET method does not always provide an accurate surface area estimation, especially for large-surface area MOFs. In this work, we propose, for the first time, a data . For example, commercial grade zinc oxide has a surface area range of 2.5 to 12 m 2 /g while nanoparticle zinc oxide can have surface areas as high as 54 m 2 /g . The nanoparticles have superior UV blocking properties when compared to the bulk material, making them useful in applications such as sunscreen. . In BET surface area analysis .
The nanoparticles’ surface area was measured by an ASAP 2010 analyzer from Micrometrics Instrument Corporation. Results and discussion. XRD analysis. . The BET analysis shows that bentonite and montmorillonite’s surface area was 46.326 and 11.325 m 2 g −1, respectively, . Therefore, the BET surface area obtained from N 2 or Ar isotherms can prove unreliable. An alternative way to characterize such materials is by implementing CO 2, which was reported for porous carbons. 142 However, reports exist where authors claimed that by employing the latter method, the BET surface area can be inaccurate. 118
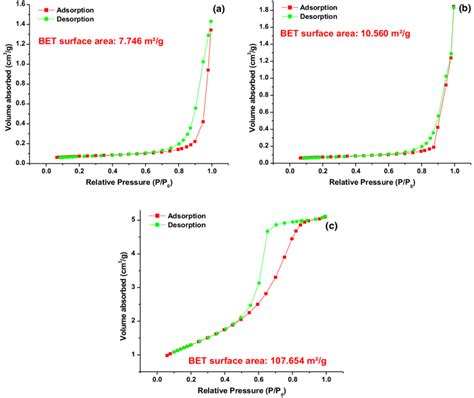
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) Surface Area Analysis and Barrett-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) Pore Size and Volume Analysis Testing Technique. . Full BET surface area characterization of disperse, nonporous or macroporous materials pore diameter >50nm (type II isotherms) and mesoporous materials with pore diameter between 2 nm and 50 nm (type IV . Pore Volume and Specific Surface Area. Pore volume (V p) and specific surface area (SSA BET) were measured from the dried nanoparticle samples with nitrogen sorption measurements (TriStar 3000, Micromeritics Inc.).Specific surface area was calculated according to the BET theory [], and pore volume was taken as the total adsorbed amount at a . The specific surface area (SSAs) of the synthesized CuO nanopowders after calcination, as well as after ultrasonic treatment and subsequent drying in air, were determined by BET analysis. The textural properties of the prepared ZrO 2 nanoparticles are examined by the BET surface analysis. Fig. 5 shows the BET surface area analysis of prepared ZrO 2 nanoparticles. The surface area (S BET), pore volume and pore diameter are estimated using the BET isotherm. The ZrO 2 nanoparticles exhibited a type IV isotherms (p/p0 = 0.50–0.95 . The BET specific surface area for this material was 133–144 m 2 /g, while the total pore volume was 0.112–0.185 cm 3 /g. But after sulphidation process, the BET surface area reduced to 110 m 2 /mg and the pore volume decreased to 0.096 cm .Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area analysis . 80 1000 800 600 400 200 PluS nanoparticles linked Porphyrin 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 40 0 0 0.5 1 Relative Pressure (P/Po) 1.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 Relative Pressure P/Po 14 Application Sample PluS NPs PluS NPs-Porphyrins Surface area (m2/g) 330.0 Pore size (nm) 18.9 192.5 2.4 14 Quantachrome Gas . Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) specific surface area analysis was performed using ‘Autosorb-1 Quanta-chrome der Firma’ equipment manufactured in the USA. The samples were analysed under nitrogen atmosphere (adsorption-desorption isotherms at 77 K) in a volumetric working device. The moisture content in the samples was removed by drying them .
The BET analysis of the data obtained by a sorption analyzer was used for the nanoparticles’ surface area determination. In relation to the catalytic activity of nanoparticles, the specific surface area was the most important quantity. The results of the measurements can be seen in Figure 6. The most significant surface area change appeared .
Synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by X-Ray diffraction spectroscopy (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area analysis. The amorphous silica nanoparticles were of 50–60 nm in diameter with .
Synthesized magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles by a simple pH-controlled precipitation method using Mg (SO4)2 as a precursor. The XRD spectra of MgO recorded at room temperature showed FCC structure. Crystallite size for synthesized MgO was calculated using Scherrer and Williamson-Hall method. The Rietveld refinement was carried . The specific surface area of CuO NPs was measured using the BET (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller) technique. The BET plot of all the samples is illustrated in Fig. 12. The multipoint adsorption method for specific surface area evaluation was used to analyze the dry and degassed samples.
BET surface area (S BET ) and pore structure properties of the activated carbons with different parameters Sample BET surface area, S BETHevira et al. (2021) reported that the speci c surface area . Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) specific surface area analysis of different graphene materials: A comparison to their structural regularity and electrical properties . Decorating ketjen black with ultra-small Mo 2 C nanoparticles to enhance polysulfides chemisorption and redox kinetics for lithium-sulfur batteries. Journal of Energy . The surface area was found to be 40.96 m 2 /g of biogenic CeO 2 NPs, much higher than the commercial CeO 2 NPs (8.5 m 2 /g) . BET was also used to measure the surface area of SiO 2 NPs produced by rice husk, CuO NPs produced by Leucaena leucocephala leaf extract, and Ag NPs produced by Acanthospermum hispidum leaf extract.